Peer Review Process
Peer review is defined as obtaining advice on individual manuscripts from reviewer’s expert in the field who are not part of the journal’s editorial staff. Peer review exists to ensure that journals publish good science which is of benefit to entire scientific community. AFRJBS aims to provide the best possible service to authors of original research articles, and the fairest system of peer review, with subject experts and dedicated Editorial Board of internationally renowned scientists.
AFRJBS Peer Review Process
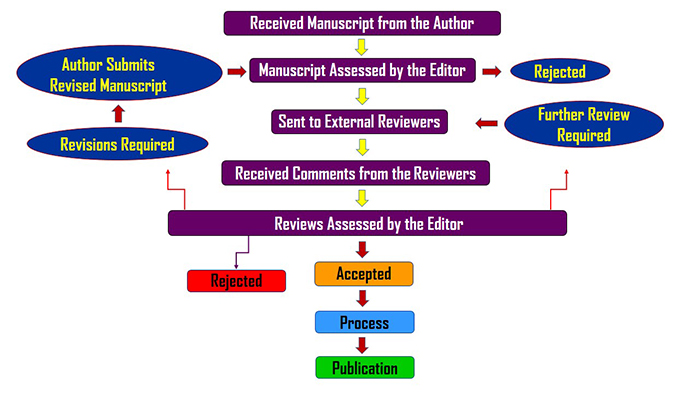
Through the peer-review process, manuscripts should become:
More robust: Peer reviewers may point out gaps in your paper that require more explanation or additional experiments.
Easier to read: If parts of your paper are difficult to understand, reviewers can tell you so that you can fix them. After all, if an expert cannot understand what you have done, it is unlikely that a reader in a different field will understand.
More useful: Peer reviewers also consider the importance of your paper to others in your field and can make suggestions to improve or better highlight this to readers.
Of course, in addition to offering authors advice, another important purpose of peer review is to make sure that the manuscripts published in the journal are of the correct quality for the journal’s aims.
Different types of peer review
There are different forms of peer review used by journals, although the basis is always the same, field experts providing comments on a paper to help improve it. The most common types are
Single blind – where the reviewers are aware of the authors’ identities but the authors do not know who reviewed their manuscript.
Double blind – in this case neither authors nor reviewers know each other’s identities.
Open – where there reviewers are aware of the authors’ identity and the reviewers’ identity is revealed to the authors. In some cases journals also publish the reviewers’ reports alongside the final published manuscript.
Key peer-review policies include the following:
There are 2 stages of review process. The first stage is internal review. In the first stage we will check the plagiarism and the suitability of the paper. If we find any plagiarism we shall return the paper to author asking him/her to modify it.
The second stage of review is the external refereeing. Under this the paper will be sent to external referees for double blind refereeing. The referee has three options; he can give the feedback as accepted/rejected/need to be revised. If the referee accepts the paper, it would be published automatically. If the referee suggests any modifications or revisions in the paper, the author has to revise the paper and resubmit to us. If the referee rejects the paper, we shall return to the author with comments.

